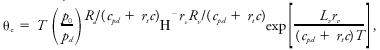Equivalent potential temperature: Difference between revisions
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
Ametsocadmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:equivalent potential temperature}} | |||
(''Also called'' [[wet-equivalent potential temperature]].) A thermodynamic quantity, with its natural [[logarithm]] proportional to the [[entropy]] of [[moist air]], that is conserved in a [[reversible moist-adiabatic process|reversible moist adiabatic process]].<br/> It is given most accurately as <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee56.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee56]]</blockquote> where θ<sub>''e''</sub> is the equivalent potential temperature, ''c''<sub>''pd''</sub> is the [[heat capacity]] at constant [[pressure]] of [[dry air]], ''r''<sub>''t''</sub> is the [[total water mixing ratio]], ''c'' is the heat capacity of liquid water, ''T'' is the [[temperature]], ''R''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for dry air, ''p''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[partial pressure]] of dry air, ''p''<sub>0</sub> is a reference pressure (usually 100 kPa), ''L''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[latent heat]] of [[vaporization]], ''r''<sub>''v''</sub> is the vapor [[mixing ratio]], ''R''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for [[water vapor]], and Η is the [[relative humidity]]. Neglect of the quantity ''r''<sub>''t''</sub>''c'', where it appears, yields a simpler expression with good [[accuracy]].<br/> Paluch, I. 1979. J. Atmos. Sci.. 36. 2467–2478. <br/> Emanuel, K. A. 1994. Atmospheric Convection. Oxford University Press, . 580 pp. <br/> | (''Also called'' [[wet-equivalent potential temperature]].) A thermodynamic quantity, with its natural [[logarithm]] proportional to the [[entropy]] of [[moist air]], that is conserved in a [[reversible moist-adiabatic process|reversible moist adiabatic process]].<br/> It is given most accurately as <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee56.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee56]]</blockquote> where θ<sub>''e''</sub> is the equivalent potential temperature, ''c''<sub>''pd''</sub> is the [[heat capacity]] at constant [[pressure]] of [[dry air]], ''r''<sub>''t''</sub> is the [[total water mixing ratio]], ''c'' is the heat capacity of liquid water, ''T'' is the [[temperature]], ''R''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for dry air, ''p''<sub>''d''</sub> is the [[partial pressure]] of dry air, ''p''<sub>0</sub> is a reference pressure (usually 100 kPa), ''L''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[latent heat]] of [[vaporization]], ''r''<sub>''v''</sub> is the vapor [[mixing ratio]], ''R''<sub>''v''</sub> is the [[gas constant]] for [[water vapor]], and Η is the [[relative humidity]]. Neglect of the quantity ''r''<sub>''t''</sub>''c'', where it appears, yields a simpler expression with good [[accuracy]].<br/> Paluch, I. 1979. J. Atmos. Sci.. 36. 2467–2478. <br/> Emanuel, K. A. 1994. Atmospheric Convection. Oxford University Press, . 580 pp. <br/> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:54, 19 April 2024
(Also called wet-equivalent potential temperature.) A thermodynamic quantity, with its natural logarithm proportional to the entropy of moist air, that is conserved in a reversible moist adiabatic process.
It is given most accurately as
where θe is the equivalent potential temperature, cpd is the heat capacity at constant pressure of dry air, rt is the total water mixing ratio, c is the heat capacity of liquid water, T is the temperature, Rd is the gas constant for dry air, pd is the partial pressure of dry air, p0 is a reference pressure (usually 100 kPa), Lv is the latent heat of vaporization, rv is the vapor mixing ratio, Rv is the gas constant for water vapor, and Η is the relative humidity. Neglect of the quantity rtc, where it appears, yields a simpler expression with good accuracy.
Paluch, I. 1979. J. Atmos. Sci.. 36. 2467–2478.
Emanuel, K. A. 1994. Atmospheric Convection. Oxford University Press, . 580 pp.
temperatura potencial equivalente[edit | edit source]
(También se conoce como temperatura potencial equivalente). Es una cantidad termodinámica cuyo logaritmo natural es proporcional a la entropía del aire húmedo, que se conserva en un proceso adiabático húmedo reversible.
Se expresa con mayor precisión como
donde θe es la temperatura potencia equivalente, cpd es la capacidad calorífica a presión constante del aire seco, rt es la proporción de mezcla de agua total, c es la capacidad calorífica de agua líquida, T es la temperatura, Rd es la constante de los gases para el aire seco, pd es la presión parcial del aire seco, p0 es una presión de referencia (usualmente 100 kPa), Lv es el calor latente de evaporación, rv es la proporción de mezcla del vapor, Rv es la constante de los gases para vapor de agua y Η es la humedad relativa. Ignorar la cantidad rtc cuando aparece brinda una expresión más simple con buena precisión.