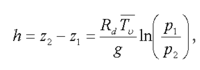Hypsometric equation: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== hypsometric equation == | == hypsometric equation == | ||
An equation relating the [[thickness]], ''h'', between two [[isobaric]] surfaces to the [[mean virtual temperature]] of the layer: <blockquote>[[File:HypsometricEqu.PNG|center|200px]]</blockquote> where ''z''<sub>1</sub> and ''z''<sub>2</sub> are geometric heights at [[pressure]] levels ''p''<sub>1</sub> and ''p''<sub>2</sub>, respectively; ''R<sub>d</sub>'' is the [[gas constant|gas constant]] for [[dry air]]; [[File:Mean_temp_HypsometricEqu.PNG|20px]] is the mean [[virtual temperature]] of the layer; and ''g'' is [[gravity]].<br/> The hypsometric equation is derived from the [[hydrostatic equation]] and the [[ideal gas]] law.<br/> | |||
'''Reference:'''<br/> | '''Reference:'''<br/> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 9: | ||
''term edited 9 December 2015'' | ''term edited 9 December 2015'' | ||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 31 March 2024
hypsometric equation
An equation relating the thickness, h, between two isobaric surfaces to the mean virtual temperature of the layer:
where z1 and z2 are geometric heights at pressure levels p1 and p2, respectively; Rd is the gas constant for dry air; is the mean virtual temperature of the layer; and g is gravity.
The hypsometric equation is derived from the hydrostatic equation and the ideal gas law.
Reference:
Wallace, J. M., and P. V. Hobbs, 1977: Atmospheric Science: An Introductory Survey. Academic Press, 55–57.
term edited 9 December 2015